| Sign In | Join Free | My himfr.com |
|
| Sign In | Join Free | My himfr.com |
|
| Ask Lasest Price | |
| Brand Name : | Jingshida |
| Certification : | None |
| Model Number : | None |
| Price : | Negotiable |
| Delivery Time : | within one week |
| Payment Terms : | T/T |
| Supply Ability : | 100,000 tons |
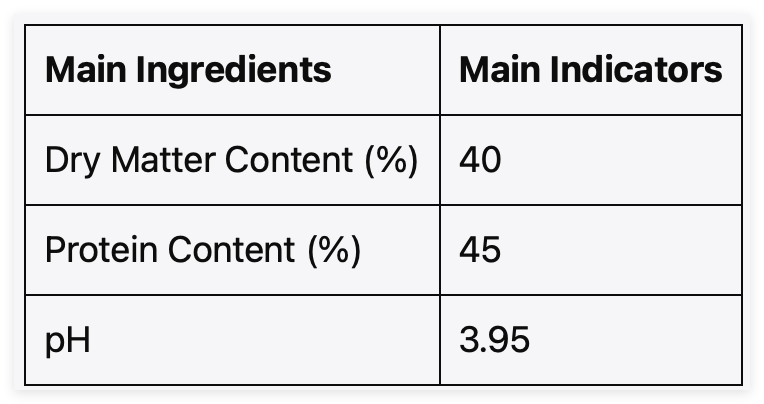
Corn syrup comes from corn and is a yellow-brown liquid.
1. Organic fertilizer and soil improvement
▪ Nutrient supplement: Corn syrup contains nitrogen, phosphorus,
potassium and organic matter. It can be directly diluted and
applied as liquid fertilizer to promote crop growth. It is
especially suitable for leafy vegetables (such as spinach and
lettuce) for rapid nutrient absorption.
▪ Microbial activator: As a carbon source and nitrogen source, it
stimulates the reproduction of probiotics (such as actinomycetes
and nitrogen-fixing bacteria) in the soil, accelerates the
decomposition of organic waste such as straw, and improves soil
fertility.
▪ Saline-alkali land improvement: Organic acids (such as lactic
acid) in corn syrup can neutralize alkaline soil, reduce pH value,
and improve salinized soil structure.
2. Seed treatment and seedling raising
▪ Seed soaking to promote germination: Diluted corn pulp is used to
soak seeds (such as wheat and rice) to provide the nutrients
required for germination, improve germination rate and uniformity
of seedlings.
▪ Seedling substrate additive: Mix with vermiculite and perlite to
make seedling substrate to enhance water retention and nutrient
slow release effect.
3. Biological pesticide carrier
Fermentation substrate: Corn pulp is a high-quality substrate for
microbial fermentation. It is used to produce biocontrol agents
such as Bacillus subtilis and Trichoderma to inhibit soil-borne
diseases (such as root rot).
1. Feed raw materials and attractants
▪ Protein and energy supplement: Corn pulp contains 20-30% soluble
protein and sugars, which can be used as a cheap protein source for
fish and shrimp feed, replacing part of fish meal and reducing feed
costs.
▪ Attractant effect: The natural aroma of sugar and amino acids
attracts fish and shrimp to eat, improves feed utilization, and is
especially suitable for carnivorous fish (such as sea bass and
mandarin fish).
▪ Fermented feed raw materials: mixed with soybean meal and bran
for fermentation to produce probiotics and small peptides, which
can enhance the intestinal health of aquatic animals.
2. Water quality control and algae cultivation
▪ Carbon source supplementation: Sprinkle corn slurry (1-2kg per
mu) into the water body to provide carbon source for beneficial
bacteria (such as nitrifying bacteria) and promote the degradation
of ammonia nitrogen and nitrite.
▪ Plankton cultivation: As a component of the culture medium of
rotifers and cladocerans, it can rapidly proliferate natural bait
and reduce the cost of bait in the seedling stage.
3. Disease prevention and control
Immunity enhancement: β-glucan and vitamin B group in corn slurry
can enhance the nonspecific immunity of fish and shrimp and reduce
the occurrence of vibriosis and white spot syndrome.
1. Feed energy and protein supplement
▪ Liquid feed additive: directly add to drinking water or mix with
feed (addition amount 3-5%) to provide easily digestible sugars and
amino acids for pigs and poultry, especially suitable for fattening
and lactating animals.
▪ Application in ruminants: corn slurry is mixed with urea to make
a slow-release nitrogen source, which improves the efficiency of
rumen microbial protein synthesis and increases the milk production
of dairy cows or the daily weight gain of beef cattle.
2. Fermented feed and silage improvement
▪ Silage additives: corn slurry contains natural substrates for
lactic acid bacteria, which can accelerate silage fermentation,
reduce pH, inhibit spoilage bacteria, and improve the quality of
silage (such as corn straw silage).
▪ Solid fermentation substrate: mixed with bean dregs and
distiller's grains to produce high-protein feed, degrade
anti-nutritional factors (such as trypsin inhibitors), and improve
nutritional value.
3. Intestinal health and environmental emission reduction
▪ Prebiotic effect: Oligosaccharides in corn slurry promote the
proliferation of intestinal lactic acid bacteria and reduce the
diarrhea rate of livestock and poultry (such as weaning stress in
piglets).
▪ Manure treatment: Feed with corn slurry can reduce ammonia
emissions in manure, and at the same time, it can be used as a
fermentation promoter for manure composting to accelerate the
decomposition of organic matter.
1. Concentration control:
Agriculture: Foliar spraying needs to be diluted 10-20 times to
avoid leaf burning due to high concentration.
Aquaculture: Excessive spraying may cause eutrophication of water
bodies and trigger algae outbreaks.
Animal husbandry: Adding more than 8% may cause diarrhea in animals
and require gradual domestication.

|